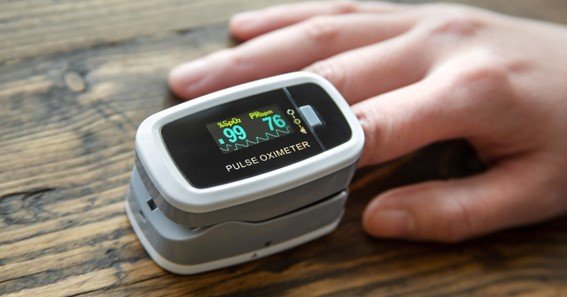
The term pulse total oxygen supply refers to the process of measuring the oxygen levels in your blood using a pulse oximeter, a non-invasive device that clips onto your finger or earlobe. This device calculates the oxygen saturation (SpO2) in your blood and gives a reading of how effectively your lungs and heart are delivering oxygen throughout your body.
A pulse oximeter measures the percentage of oxygen in your blood by emitting light through your skin and detecting how much oxygen is bound to your red blood cells. Normal oxygen saturation levels typically range from 95% to 100%, and readings below 92% can indicate low oxygen levels or hypoxia, which may require medical attention.
Why is Pulse Total Oxygen Supply Important?
Monitoring the total oxygen supply through pulse oximetry is crucial for individuals with heart or lung conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, or pneumonia. It helps healthcare providers assess whether the body is receiving enough oxygen and if interventions like supplemental oxygen or ventilators are necessary.
“Pulse Total Oxygen Supply” refers to the total amount of oxygen delivered to the body during each heartbeat, crucial for understanding respiratory efficiency.
FAQ
- What does a pulse oximeter measure?
It measures the oxygen saturation (SpO2) level in the blood, reflecting how well oxygen is being transported to the organs and tissues. - What is a normal oxygen level reading?
Normal readings usually fall between 95% and 100%. A reading below 92% may suggest that the oxygen supply is insufficient. - Why is my pulse oximeter reading low?
A low reading could indicate respiratory issues such as hypoxia. Conditions like asthma, pneumonia, or heart problems can cause this. Environmental factors like high altitudes can also result in lower readings. - How does a pulse oximeter work?
The device shines light through your skin to measure how much light is absorbed by oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, calculating the percentage of oxygen saturation. - Can I use a pulse oximeter at home?
Yes, especially for monitoring chronic conditions that affect lung function, like COPD or asthma. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider on how to interpret results and when to seek medical attention.
Understanding the pulse total oxygen supply through pulse oximetry is essential for managing respiratory and cardiovascular health. By keeping track of your oxygen levels, you can ensure that your body is receiving the necessary oxygen to function properly.